Testicular Cancer Symptoms and First Signs
Testicular cancer does not always have symptoms. Usually the disease manifests itself like a tumor in the testis, which is the first of testicular cancer symptoms. This swelling is painless. In addition, among the manifestations of cancer may be noted such testicular cancer symptoms:
- An enlargement of a testicle
- A significant shrinking of a testicle
- A change in the consistency of a testicle
- Pain or discomfort in lower abdomen or in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in a testicle
Some types of testicular cancer are characterized by increased production of hormones (e.g. chorionic honodotropin (HGT), estrogen, testosterone). Raising HGT level, for example, may be manifested in an increase in the breast. Elevated levels of estrogen can reduce libido (sex drive), while increasing the level of testosterone leads to premature puberty in boys, as reflected, for example, hair growth on face and body.
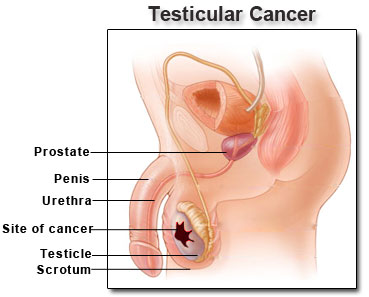
Most often, the tumor does not cause any painful sensations, they arise when the cancer is transferred to the testicular cord, elements of which include nerves. Later – testicle becomes very dense, it deforms. Then, the boundary between the testis and its appendage disappear, and between the shells of eggs accumulated fluid.
Approximately 3% of cases the tumor developed at once in both testicles, but it may be the appearance on one side and a few years later. In metastatic cancer pain can be observed in their respective fields. For example, with metastases in the vertebrae of pain found in the back, with metastases to the lungs – the hemoptysis, or shortness of breath, and coughing.
Dutch researchers have found that men, who have experienced testicular cancer, have a moderately increased risk of myocardial infarction at a young age.
Flora E. van Leeuwen of the Dutch Cancer Institute (Amsterdam) studied the information on the 2512 men who have experienced cancer of the testicles, and treated between 1965 and 1995. Compared with men, not to transfer testes cancer, those who moved in almost 2-fold increased risk of myocardial infarction before the age of 54 years. The irradiation of the chest (with metastases to the lungs), increased the risk 3.7 times compared with only surgical treatment. The irradiation of the abdomen and the lower half of the body will not affect the risk.
There are several versions explaining the relationship between infarction and testicle cancer. In men, cancer of the testicles has experienced very frequent classical factors of cardiovascular risk, – Note the authors. In addition, several years after chemotherapy, there is a violation of the functions of blood vessels and formation of atherosclerotic plaque, which can also lead to a heart attack.
How to examine yourself for testicular cancer
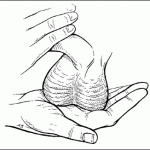
So, at what should you pay attention, while testing your testicles? First of all, the eggs should be roughly the same. If one of them is abnormally low, it is likely atrophied after a long-standing infection.
 One testicle always hangs lower than the other. Otherwise you could not put the legs together. Inspect yourself every month, but only in a warm place – on a cold scrotum severely cringe. Perfectly to conduct inspections, while taking a bath or shower.
One testicle always hangs lower than the other. Otherwise you could not put the legs together. Inspect yourself every month, but only in a warm place – on a cold scrotum severely cringe. Perfectly to conduct inspections, while taking a bath or shower.
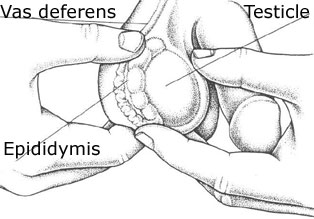
Set between the testicles and other large fingers. They must be felt as boiled egg (without shell, of course) about 3,5-4 cm in diameter, the size should not vary by more than 5-6 mm.
 Touching the back top of the testicle, you’ll find appendage testis – a thin funicle. If you can easily find it, you can just let it go – anything attached to appendage or free lying next to it, almost certainly benign (unfortunately, this can not be said about the entities associated with the testicle). Inside the appendage there is a tortuous duct, which connects the top of the testicle with a thick spermoduct.
Touching the back top of the testicle, you’ll find appendage testis – a thin funicle. If you can easily find it, you can just let it go – anything attached to appendage or free lying next to it, almost certainly benign (unfortunately, this can not be said about the entities associated with the testicle). Inside the appendage there is a tortuous duct, which connects the top of the testicle with a thick spermoduct.
If you find an unusual swelling, bumps or other abnormality, conduct a simple diagnostic test. Go to a dark room. Turn the pocket lamp and place it behind the scrotum. If the light easily passes through it, the tumor, most likely filled with liquid – a symptom typical of harmless hydropsy testicle cyst or seed funicle. But even in this case, you’d better visit the doctor.
 Very few of the testicles are malignant tumors, but doctors examine and treat any of them as cancer, before getting the lasts and right results. Fortunately, an experienced urologist or surgeon can confidently diagnose the majority of the benign entities immediately upon inspection at the hospital.
Very few of the testicles are malignant tumors, but doctors examine and treat any of them as cancer, before getting the lasts and right results. Fortunately, an experienced urologist or surgeon can confidently diagnose the majority of the benign entities immediately upon inspection at the hospital.
In doubtful cases, the doctor reveals the scrotum in order to make the more detailed examination of testicles. If doubts remain after that, the doctor may remove a suspicious testis and its spermoduct. In cases of suspected testis cancer, doctors do not biopsy because the chances of spread of malignant cells are very large.
 Although some patients complain of pain and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, almost all cases of testicles cancer begin with the appearance of painless tumors. The man conducting self examining, are unlikely to feel the other symptoms (back pain, cough, weight loss), because all they usually indicate nothing of the appearance of metastases.
Although some patients complain of pain and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, almost all cases of testicles cancer begin with the appearance of painless tumors. The man conducting self examining, are unlikely to feel the other symptoms (back pain, cough, weight loss), because all they usually indicate nothing of the appearance of metastases.
So, you should turn to your doctor in case of tentative symptoms of testicular cancer:
• If you have found an increase of one of the testicles;
• Study is painful;
• If you feel papilla, which did not feel up to this;
• If you have a sense of «gravity» in the scrotum;
• When you are standing at the bottom of stomach pains in the inguinal area;
• If you notice blood in the urine;
• Increasing breast.
Tumors of testis may be benign and malignant. Remember, only the doctor has the right to putt diagnosis «testicle cancer». The regular monthly self examining and immediate access to a doctor in case of detection of one of these signs to prevent the development of malignant tumors, and in the case of early detection – to achieve a complete cure.
There is no way to prevent cancer of the testicles – the only protection is early detection.
A lot of men – but not prudent women! – reach middle age, never having visited a doctor, and this difference in behavior is almost entirely due to the difference in the genitals. Women’s genitals are in need of constant and regular attention. A woman, even with perfect health should visit doctors each year to check the breast and taking of smears from the vagina.
And finally, a healthy woman visited a doctor yet to either prevent or interrupt, or to maintain the pregnancy. Looking at the apparently endless demand their girlfriends in the health services, young people are grateful to fate for having had urogenital system, requiring very little concern. But for such “luck” they would have to pay later!
Upon noticing the usual warts on the penis, the man immediately goes to the doctor. However, painless swelling in the testicles can grow to impressive size, but its unlikely cause the same concern. Almost all such tumors are harmless, but still about a thousands Americans each year develop testicular cancer – the most common malignant tumor for men from 15 to 34 years.
If you can find a similar – you are lucky, because almost 100% of the detected at an early stage of testicular cancer successfully cured. Usually the late detection of prognosis is not as favorable.
Sex in itself, and sexually transmitted diseases, do not concern anything to testicle cancer. Men born with cryptorchism, are ten times risked cancer than the rest. Surgical correction does not reduce the risk, while facilitating the detection of tumors. Since only 10% of men with cancer of the testicles that are inherent in violation, the others should not forget about risk. Men tend to say, that first they had an illness of the testes and only later discovered the tumor.
On the other hand, scarring and atrophy of tissues in the field of trauma, later, may cause changes that promote malignant transformation of cells. Men, who has the atrophy of testicles, and those who have mumps, followed by inflammation of the testicles – orchids, it seems, are more at risk. There is no way to prevent cancer of the testicles – the only protection is early detection.
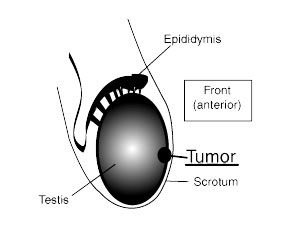
What are the testicular cancer symptoms? In other words, if any changes in their testicles man should always consult a doctor? You must be alert the following changes: the presence of a smooth seal (hard) in the testis tissue, a significant change in testis size (increase or decrease); accumulation of fluid in scrotum (edema), long, moderately expressed, nagging pain in the scrotum without apparent reason. Typically, the tumor occurs in only one testicle, very rarely may be bilateral changes in the scrotum.
Testicular cancer – self-identified evil
This disease, the main reason for which became tumors in the testicles atypical cells, leads to densification and swelling. Atypical cells may occur in different organs. Cancer of the testicles – the most widespread malignant tumor that occurs in men older than 35 years.
Cause of testicles cancer has not been established. The development of atypical tumor cells is a cause of increasing the development of the testicles, or seals, which can feel and identify visually. Men suffering from such disease or experienced as cryptorchrism, regardless of whether surgical intervention, constitute the “risk” in the exercise of testis neoplasms.
Cryptorchrism – is a pathological condition in which both testicles of the child haven’t fell from the abdominal cavity in the scrotum, which usually occurs in the womb before birth.
 The testicular cancer symptoms are: seal directly on the testis, which is not painful, but from time to time is a feeling of discomfort, decreasing one of the testes after puberty, in some cases there has been chest increasing.
The testicular cancer symptoms are: seal directly on the testis, which is not painful, but from time to time is a feeling of discomfort, decreasing one of the testes after puberty, in some cases there has been chest increasing.
In the process of cancer development there are such symptoms as pain in the lower back and discomfort, difficulty with urination, cough or breathing problems.
Testicular cancer can be diagnosed with a doctor who is familiar with the history of the patient and conducts regular inspections of the testicles, and if necessary examinations of other organs and systems. The doctor may also insist on carrying out laboratory research, such as blood tests, x-ray studies of kidney, urethra, thorax, pelvic organs, or bone tissue. Treatment is assigned depending on the stage of disease. In some stages of the disease testicles may be amputated.
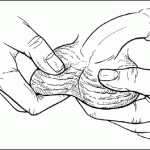
As the result of treatment depends on early diagnosis of the disease before its distribution, for men are an important monthly self examination of the testicles. The procedure is simple: keeping eggs with one hand, you have to touch each other from one hand to another.
At the same time you should feel epididimis (shell) that covers the top, back and bottom of the testicle. Carefully carry the shell using your fingers and touching the testicle itself. If you find seals in the testicle, usually painless, refer urgently to a doctor. You must undergo regular medical check-ups, especially if you suffer from cryptorchism.
